Securities Lending - Unlocking Portfolio Potential
A well-managed securities lending programme can be a valuable portfolio management tool, and may enable funds to receive an additional source of income that may add incremental risk-adjusted returns to a fund’s overall investment return objective.
Why does PAIF Participate in Securities Lending?
Since 10 July 2018, ABF Pan Asia Bond Index Fund (PAIF) has operated a securities lending programme, which has been designed to manage the fund to the potential benefits of securities lending while mitigating associated risks. The fund may generate income from the securities lending program, which may offset some of the associated costs of fund operations and potentially enhance its returns. The addition of Asian local-currency denominated bonds into the lending pool may deepen liquidity in the secondary markets.
Securities Lending Revenue and Costs
All revenues that may arise from securities lending in respect of an ETF, net of direct and indirect operational costs, will be returned to the fund.
- 70% of the total income received from securities lending transactions will be credited to the account of the Trust. The balance of any such income will be for the account of the securities lending agent.
- No income from securities lending transactions accrues to the Manager.
What is Securities Lending?
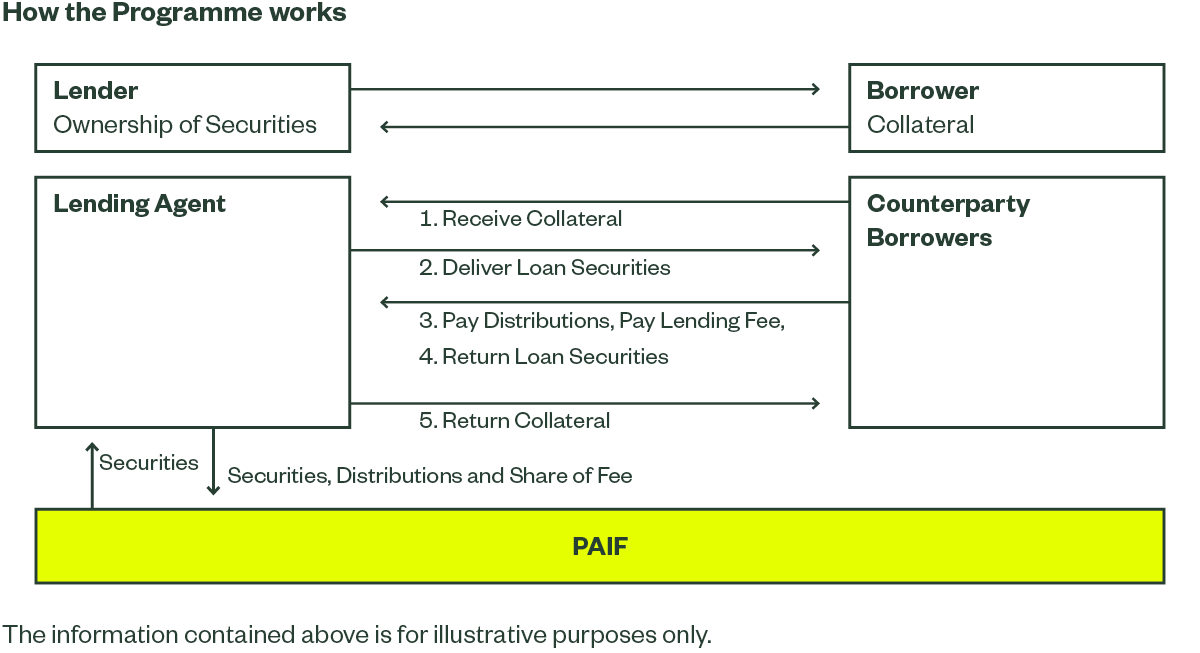
A securities lending transaction involves the temporary transfer of securities from one party (the lender) to another party (the borrower). Securities lending enables funds enrolled in the securities lending programme (the lender) to potentially generate an additional source of income.
In all cases, the securities borrower is a financial intermediary, such as a broker, dealer or market maker. In exchange for borrowing the securities from a fund, the borrower transfers collateral to the lending agent who holds that collateral in an account in the fund’s name. The borrower pays a fee for borrowing the securities and is contractually obliged to return the loaned securities. The loan is usually arranged by the securities lending programme coordinator, known as a lending agent.
During the term of the loan, the borrower must provide collateral to the funds to mitigate against the risk of non-return of any loaned securities. The borrower receives all distributions and dividends arising during the period of the loan and pays these amounts to the lending agent at the same rate as if the securities were held in custody. The lending agent then pays all distributions and dividends on to the underlying lender. The borrower will generally have the right to exercise any voting rights arising during the period of the loan that relate to the loaned securities.
Governance
The State Street Global Advisors’ Global Investment and Product Committee (Committee) oversees and comprehensively reviews performance and effectiveness, and provides oversight of State Street Global Advisors’ Global Securities Lending programmes.
The Committee evaluates the performance of State Street Global Advisors’ securities lending agents. It also reviews and challenges State Street Global Advisors’ Global Securities Lending programmes against industry standards and performance, current risk appetite levels, and current market conditions.
In addition, the securities lending programme for each participating fund is reviewed, approved and overseen by the respective fund boards.
Collateral
In general the minimum acceptable collateral currently accepted are:
- Government securities and Supranational debt issued or guaranteed by an entity or trust that has a minimum long term rating of: “A” by Moody’s, “A” by Standard and Poor’s, or “A” by Fitch including sub-categories or gradations therein.
Collateral Margin Requirements
The collateral amount is marked to market daily. If collateral levels are insufficient for a particular loan, the borrower is required to provide more collateral. If the loan is over- collateralised, the lending agent may return some of the collateral to the borrower.
- Government securities transferred as collateral shall have a minimum collateral market value of not less than 102.5% of the loaned securities.
Securities Lending Report
The Securities Lending Report is updated on a monthly basis and available on abf-paif.com.
Indemnification
HSBC PLC (acting through its securities service division) provides a counterparty default indemnity. In accordance with this indemnity, if a counterparty fails to return securities lent by the fund, subject to the terms of the securities lending agreement, HSBC PLC would either purchase replacement securities for the fund, or shall credit to the fund an amount of cash equal to the market value of the securities.
Lending Limits
The percentage out on loan will depend on the type of fund and securities held but will be subject to the below limits established by State Street Global Advisors as internal guidelines for the lending programme:
- Maximum of 50% on loan for a single security of the aggregate market holding of Securities of that issue available for lending, as determined by the Securities Lending Agent and as agreed by the Trustee.
- The aggregate outstanding value of loaned securities shall not exceed 30% of its total net asset value.
Potential Risks of Securities Lending
As with all investment activities, securities lending bears risks. Here are some of the key risks and safeguards that are in place:
| Risks | Risk Mitigates and Considerations |
Counterparty or Borrower Risk Borrowing counterparty default Recall/settlement risk Collateral insufficiency Failure to provide manufactured income or entitlements |
Counterparty credit risk management Controlling the quality of approved borrowers Monitoring daily margin requirements Borrower default indemnification |
Collateral Risk Credit Liquidity |
Over collateralisation Marked to market daily |
| Failed Trade Settlement | Agent lender depth of supply Agent lender can execute buy in to force settlement |
| Reputational Risk | Comprehensive oversight and ongoing communication with the lending agent |
| Collateral Diversification | The collateral is sufficiently diversified in terms of country, markets and issuers |
Source: State Street Global Advisors, as of 31 December 2024.
While not without risk, a well-managed securities lending programme can help to unlock an additional source of income in portfolios.